News
Sci-Fi-Turbo at ASME Turbo Expo 2025
18.06.2025 The Sci-Fi-Turbo project is contributing to this year ASME Turbo Expo in Memphis, Tennessee. Georgios Goinis from DLR-Institute of Propulsion Technology presented a joint paper related to the project’s dissemination activities: 𝗘𝘅𝗮𝗺𝗶𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗣𝗼𝘁𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗮𝗹 𝗼𝗳 𝗛𝗶𝗴𝗵-𝗢𝗿𝗱𝗲𝗿 𝗦𝗥𝗦 𝘁𝗼 𝗦𝘂𝗽𝗽𝗼𝗿𝘁 𝗥𝗔𝗡𝗦-𝗕𝗮𝘀𝗲𝗱 𝗖𝗼𝗺𝗽𝗿𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗼𝗿 𝗔𝗶𝗿𝗳𝗼𝗶𝗹 𝗢𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗺𝗶𝘇𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻.
Research is international, and the challenges in aviation can only be addressed through global collaboration and knowledge exchange. That’s why the ASME Turbo Expo, bringing together over 2,000 scientists as well as representatives from industry and academia, is one of the most important conferences in the turbomachinery research field.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
International Symposium on AI and Fluid Mechanics
27.05.2025 The Sci-Fi-Turbo team participated in the 1st International Symposium on AI and Fluid Mechanics in Chania, Crete.1st International Symposium on AI and Fluid Mechanics in Chania, Crete.
Our contributions focused on the advancement of AI-enabled, scale-resolving simulation workflows in aero engine design:
🔹 Marc Schouler, PhD (Sorbonne Université) presented a multi-fidelity aerodynamic optimization approach driven by wall-resolved LES, combining a Bayesian flow emulator, dimensionality reduction, and an active learning strategy.
🔹 George Klavaris (Ansys) showcased a data-driven turbulence modeling workflow using the GEKO model, calibrated with high-fidelity LES data through adjoint-based sensitivity analysis and field inversion, and generalized across varying flow conditions via a neural network.
🔹 Georgios Goinis (DLR Institute of Propulsion Technology) discussed the use of transformer-based AI models as CFD surrogates in aerodynamic optimization, highlighting strategies to reduce computational cost and outlining key implementation challenges.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
New results presented at the European Turbomachinery Conference 2025
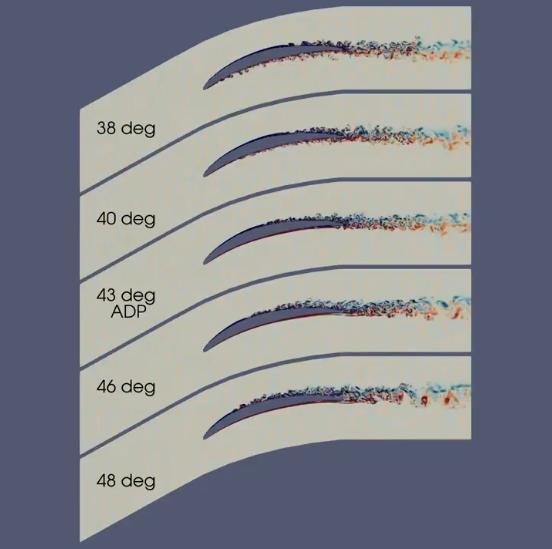
24.03.2025 New results from the Sci-Fi-Turbo project were presented at the European Turbomachinery Conference, in Hannover, Germany: A comparative study of varying incidence angle effects on a low-Reynolds-number compressor cascade based on experiments, low-fidelity and high-fidelity numerical simulations.
Michael Bergmann presented the paper, where the authors studied how high-order LES can help overcome the limitations of low-fidelity approaches at challenging design operating points.
The LES setup in TRACE is based on:
- Split-form Discontinuous Galerkin Spectral Element Method (DGSEM)
- 5th-order spatial accuracy
- Implicit LES formulation
- Synthetic inflow turbulence to reflect experimental conditions
- AVDR modeling to align numerical and experimental setups
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Sci-Fi-Turbo spirit at our workshop
19.02.2025 We are still full of inspirations from our workshop at CINECA! Here are some impressions from the incredibly motivated and innovative team of the Sci-Fi-Turbo project. It's great to work with such a dynamic and forward thinking team. We love the Sci-Fi-Turbo spirit!
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Advancing Sci-Fi-Turbo at CINECA
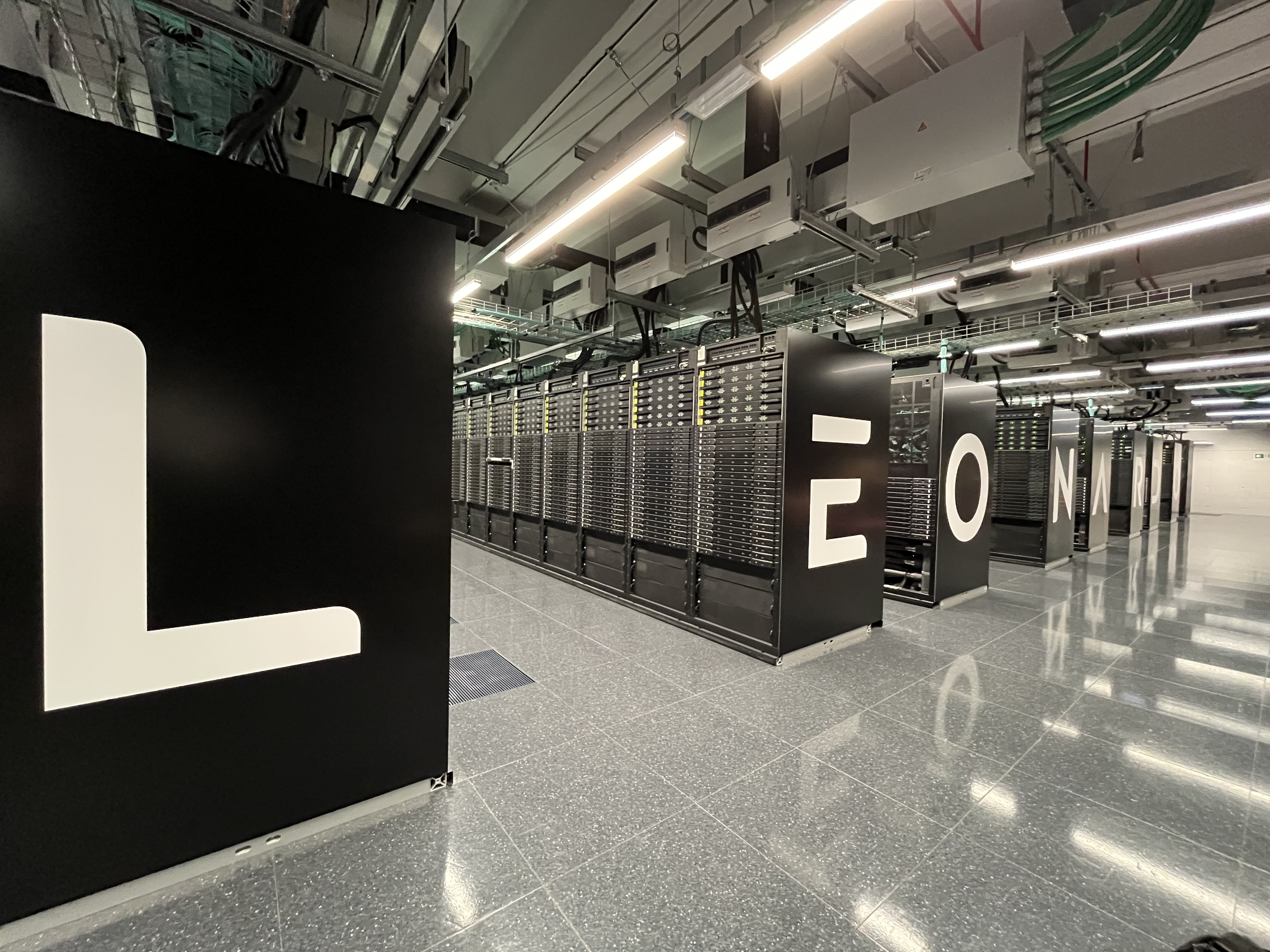
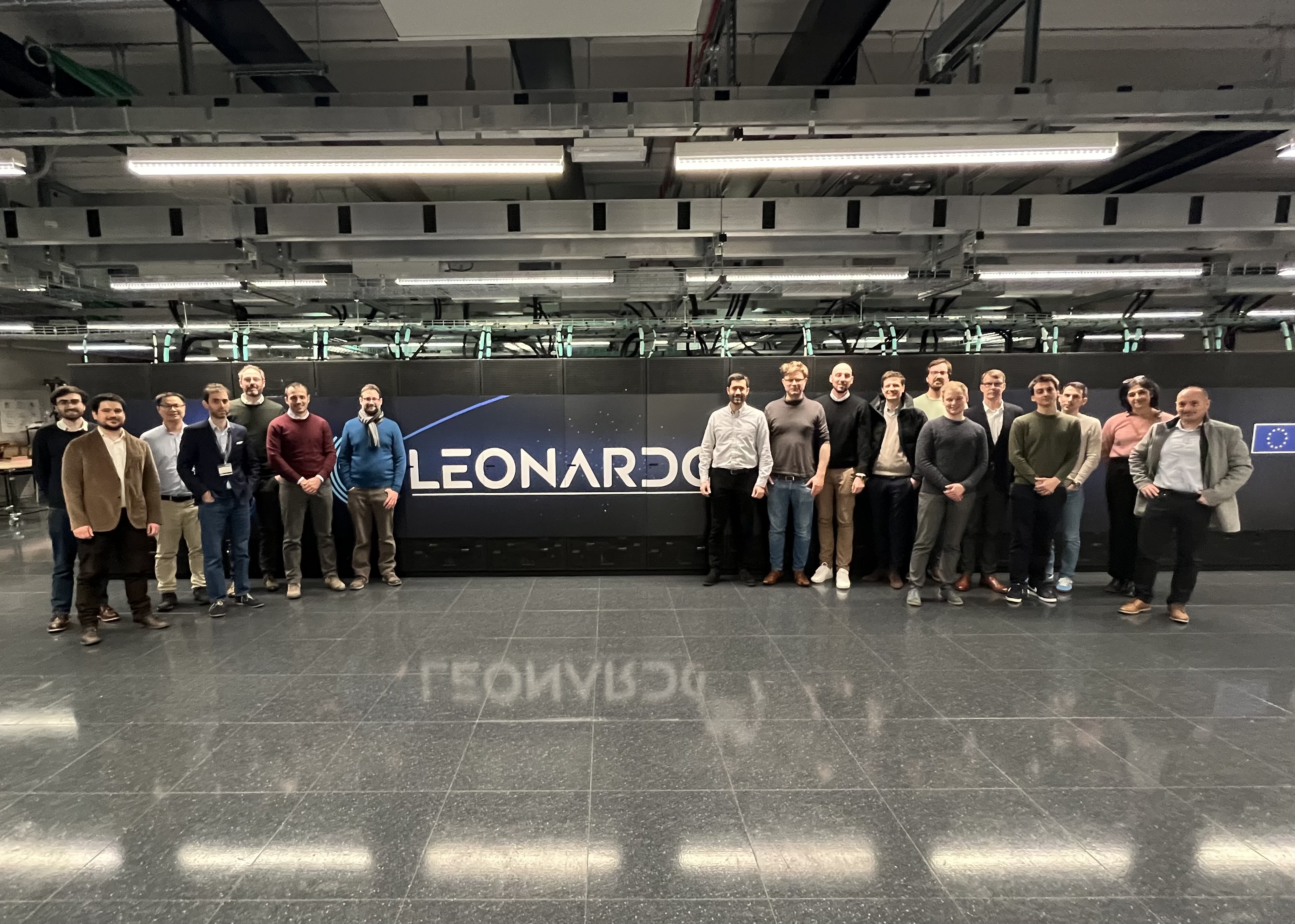
12.02.2025 It was an incredibly productive few days last week as we gathered at CINECA in Bologna for an in-person workshop. We're very excited about the progress we're making in the EU Horizon Sci-Fi-Turbo project. Our discussions focused on pushing the boundaries of efficient scale-resolving simulations for turbomachinery flows, along with advancements in multi-fidelity IA-supported optimization methodologies.
A highlight of the event was visiting the Leonardo supercomputer , one of the top 10 most powerful supercomputers in the world! Cutting-edge HPC systems play a crucial role in enabling high-fidelity simulations, helping us drive innovation for ultra-efficient propulsion systems.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Turbulence Modeling supported by Statistical Machine Learning Models
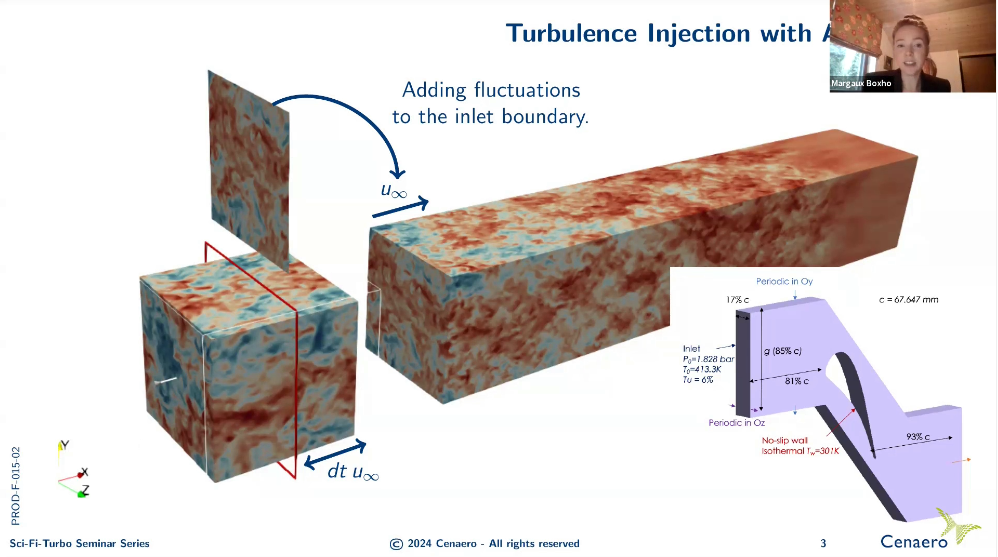
16.12.2024. Turbulence modeling is an important area of study within the fluid dynamics community. Recent advances in computational power, particularly with the development of GPUs and TPUs, have led to the emergence of Machine Learning and Deep Learning techniques as valuable tools for modeling turbulence at different stages: (i) enhancing RANS models, (ii) creating new wall models, (iii) contributing to flow control, and (iv) generating instantaneous turbulent flow fields, to cite a few. The presentation will tackle two of these challenges. The first is developing a data-driven wall model in the context of wall-modeled Large Eddy Simulations (wmLES) of turbulent separated flows. To address the instantaneous and non-equilibrium separation phenomenon, the Mixture Density Network (MDN), the neural network implementation of a Gaussian Mixture Model initially used for uncertainty prediction, is employed as the wall shear stress model. The second challenge focuses on enhancing turbulence injection methods. According to Dhamankar et al. (2015), the developed method should be memory-efficient, suitable for various flow problems, and incorporate known information about turbulence without introducing spurious low-frequency oscillations or unrealistic inflow characteristics. The generated turbulence should develop as quickly as possible after the inlet. To address this challenge, diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM) and score-based models, known to be powerful tools for generating high-quality samples while being straightforward to define and efficient to train, are selected to reproduce Decaying Homogeneous Turbulent Turbulence (DHIT) samples.
Click here for the Sci-Fi-Turbo Seminar Learning Partial Differential Equations.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Learning Partial Differential Equations
04.12.2024 I The recording of the seminar Learning PDEs by Prof. Siddartha Mishra from ETH Zürich is now available! Watch the latest talk of our Sci-Fi-Turbo Seminar Series seminar series.
PDEs are considered to be language of physics as they provide mathematical descriptions of a whole range of physical phenomena. The complexity and prohibitive computational cost of traditional physics-based numerical schemes necessitates the search for fast and efficient surrogates, based on machine learning. In this lecture, we survey recent developments in the field of learning solution operators for PDEs by focussing on structure preserving neural operators and on foundation models for sample efficient and generalizable multi-operator learning. We also briefly discuss graph neural network based learning of PDEs on arbitrary domain geometries and conditional Diffusion models for learning multi-scale physical systems such as Turbulent Fluid Flows.
Click here for the Sci-Fi-Turbo Seminar Learning Partial Differential Equations.
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________